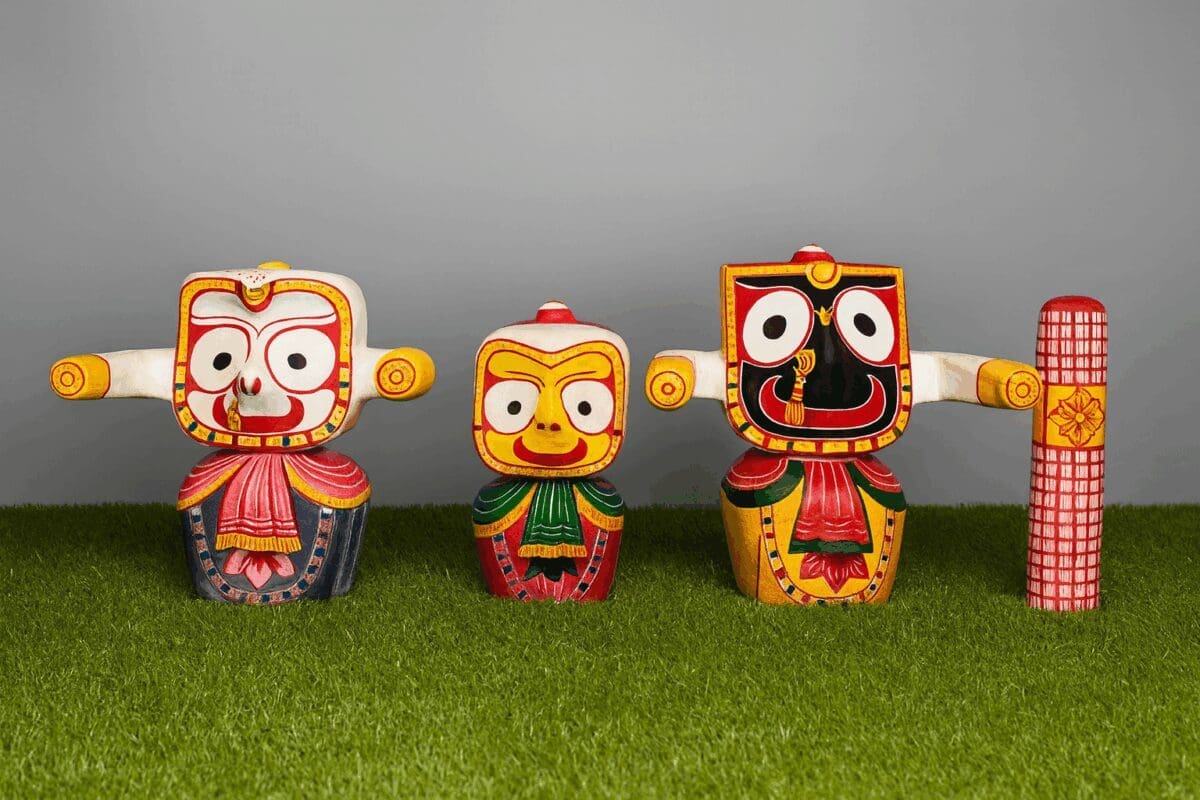
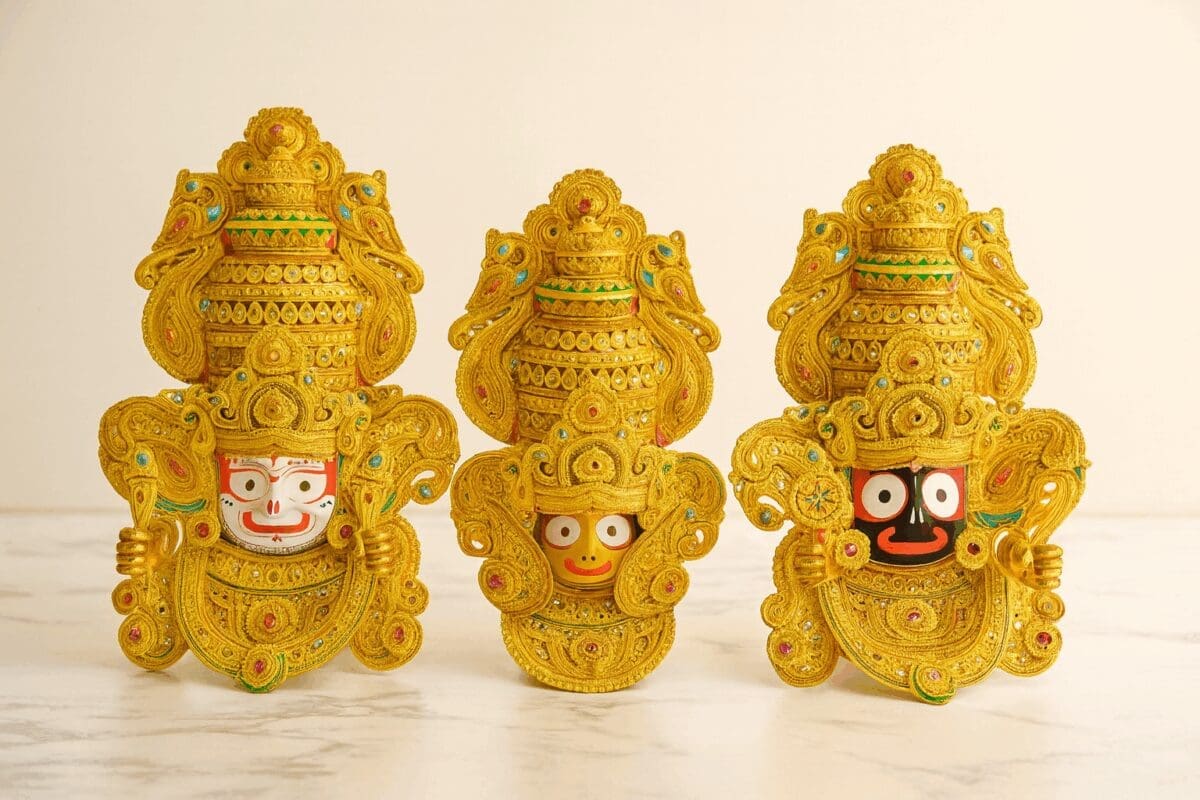
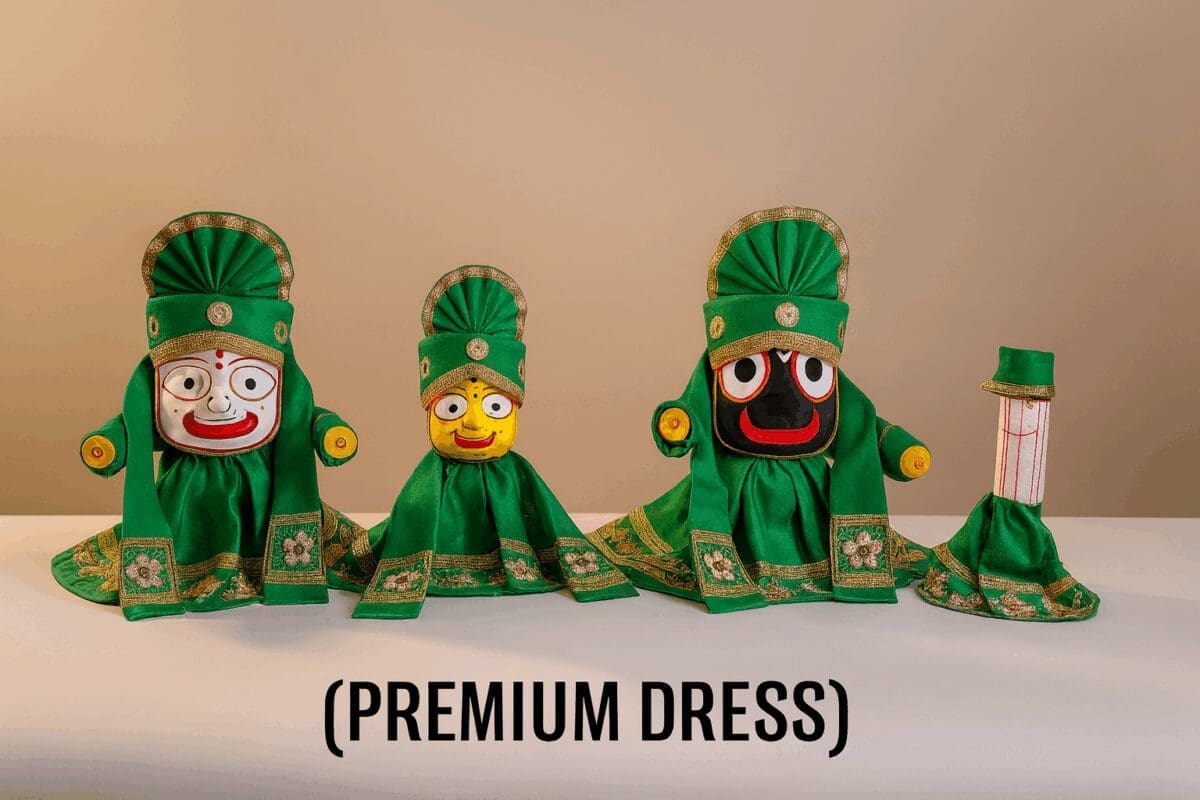
All Besha Of Shri Jagannath Mahaprabhu
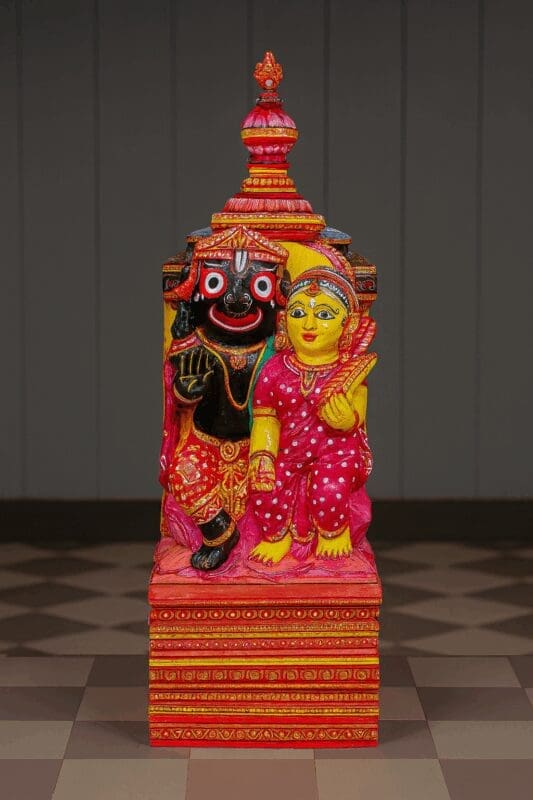
Significance of Neem in Jagannath Idols
Ancient texts like Varahamihira’s ‘Vrihat Samhita’ and Kashyapa’s ‘Shilpashastra’ prescribe ‘Daru’ (wood) as an ideal material for divine idols. The ‘Bhavishya Purana’ specifically recommends various auspicious trees for Surya (Sun God) idols, including peepul, mahua, deodar, sandal, bel, khadir, anchan, neem, sriparna, jackfruit, arjun, and raktachandan (red sandalwood).
However, Neem wood holds particular significance for the deities of the Mahaprabhu Shree Jagannath Temple. The ‘Bhavishya Purana’ states, ‘Nimbadyah Sarvavarnanam Vrikshyah Sadharanah Smrutah,’ meaning Neem wood is suitable for all social groups. This is reinforced by the ‘Pratima Lakshana Soudhagama,’ which declares, ‘Nimba pradhanmetasham pratima chabinirmitou,’ emphasizing Neem as the prime choice for idol making.
The Jagannath Temple’s rituals involve individuals from diverse backgrounds: Brahmin Vidyapati, Kshatriya King Gajapati Maharaja, and tribal Biswabashu descendants. Using Neem Daru ensures the deities’ universal accessibility, accommodating servitors and worshippers of every caste and class. This reflects the inclusive nature of the Jagannath tradition. The choice of Neem transcends mere material suitability; it embodies a profound social and spiritual message of equality and universal acceptance.